Covering an area of 1500 sq. kilometers, Tehran is situated in the north-central part of Iran. As the capital, it is the most populated city in Iran, and the center of cultural, economic, political and social activities. With its cosmopolitan atmosphere, Tehran population represents a diverse ethnic/linguistic composition of Iran.

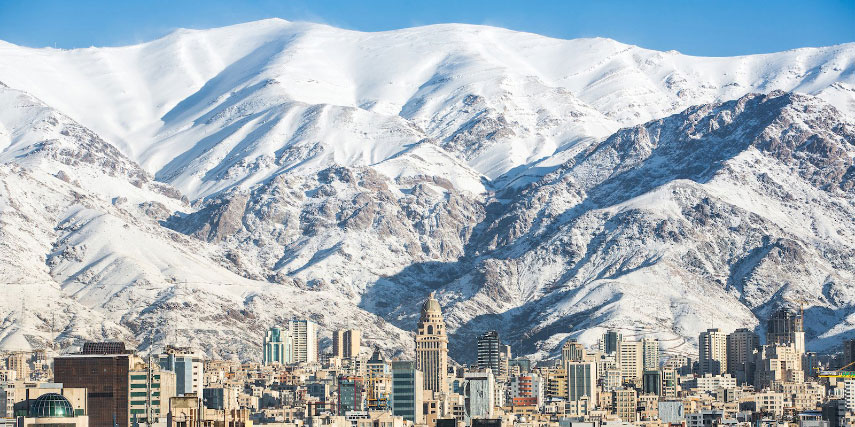
Tehran's climate is largely defined by its geographic location, with the towering Alborz Mountains to its North and the central desert to the South. It can be generally described as mild in the spring, hot and dry in the summer, cool and rainy in autumn, and cold in the winter. As a large city with significant differences in elevation among various districts, the weather is often cooler in the hilly north as compared to the flat southern part of Tehran. Summer is usually hot and dry with very little rain. The majority of precipitation occurs from mid-autumn to mid-spring. The hottest month is July (mean minimum temperature 23°C, mean maximum temperature 36°C) and the coldest is January (mean minimum temperature -1°C, mean maximum temperature 8°C)

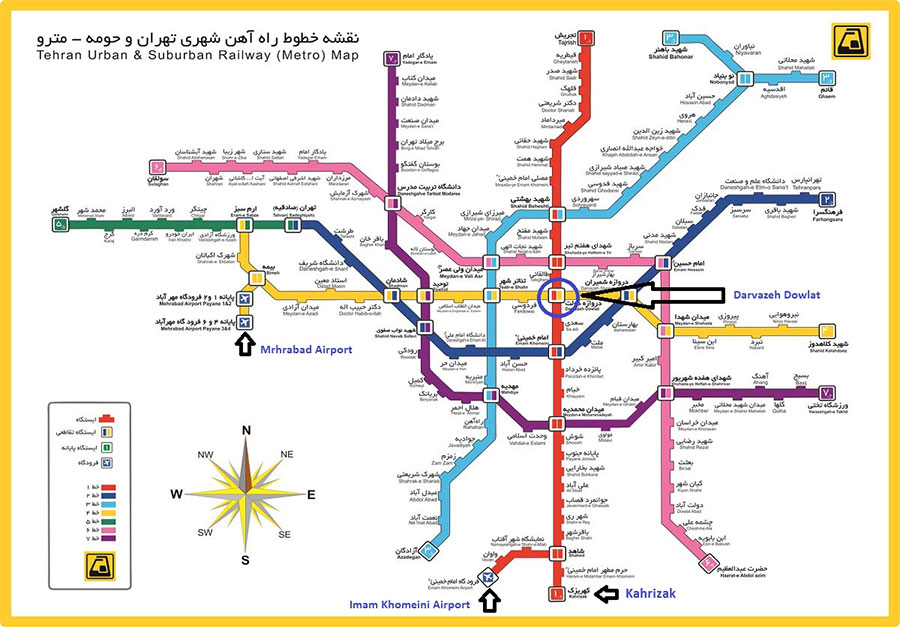
The metropolis of Tehran enjoys a huge network of highways (280 kilometers) and of interchanges’ ramps & loops (180 kilometers). In 2007, there were 130 kilometers of highways and 120 kilometers of ramps and loops under construction. Tehran has one of the cleanest and most convenient metro (underground) systems, in terms of accessibility to different parts of the city, in the region. Taxis fill the void for local journeys. Tehran is served by Mehrabad National Airport, an old airport located in the Western part of the city, and Imam Khomeini International Airport, 50 kilometers south, which handles international flights.
Since the establishment of Darolfonoon in the mid 1800s, Tehran has amassed a large number of institutions of higher education. Some of these institutions have played crucial roles in the unfolding of Iranian political events. The University of Tehran and Tehran University of Medical Sciences are the oldest state universities, and the largest universities of Iran, respectively.
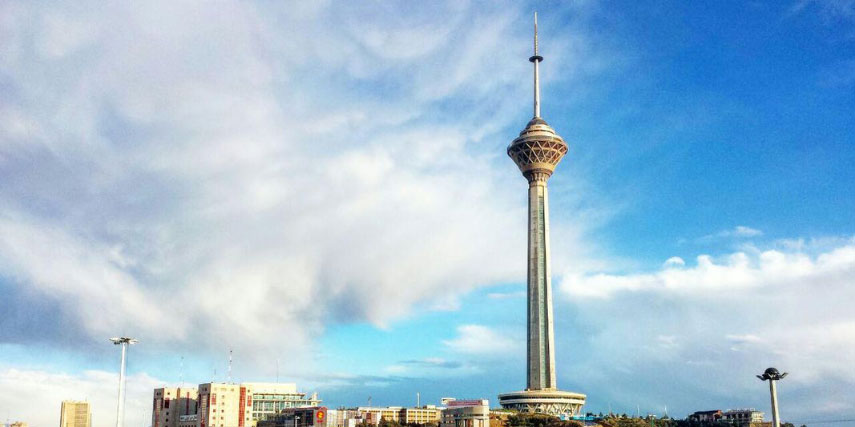
Milad complex contains the world's fourth tallest tower, several restaurants, a five star hotel, a convention center, a world trade center, and an IT park. Traditionally, a low-lying city due to seismic activity in the region, modern high rise developments in Tehran have been undertaken in order to service its growing population.

